Injection-molded plastics are plastic shapes or products that have been created during plastic injection molding, or plastic injection moulding. During the plastic injection molding process, manufacturers inject a mold cavity, which is shaped like an intended product, with molten plastic resin. Once the resin material has hardened and cooled, they remove the mold, revealing the product, which has taken the mold cavity’s shape. Read More…
For 50 years, LTM Plastics has been a leading manufacturer of injection molded plastics. When working with LTM Plastics, our customers can be assured that they are getting high quality products at a competitive price. We pride ourselves on our team’s communication and collaboration with our customers to meet their needs.

As one of the Midwest’s oldest plastic molders, Koller-Craft has craftsmanship built into its name. We take pride in our quality injection molding work. Large to small parts, short to long runs. Excelling at product design, prototyping, close tolerance molding, insert molding & secondary services.
Performance Engineered Products, Inc. is a dynamic and innovative company, and we pride ourselves on being at the forefront of the injection molded plastics industry. With a rich history dating back to 1981, we have consistently demonstrated our commitment to excellence in both products and services.
We may have started small, but today, we offer our products and services to companies around the world. We are dedicated to our customers, and our goal is to offer better service and pricing to any customer no matter the size.
Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, Inc. offers injection molding for a variety of industries. We can process an almost infinite variety of thermoplastic resins, our prices are competitive, our delivery is on time, and we provide superior customer service. Value-added services include label application, assembly services, and custom packaging and shipping. Our team has the knowledge and expertise to...
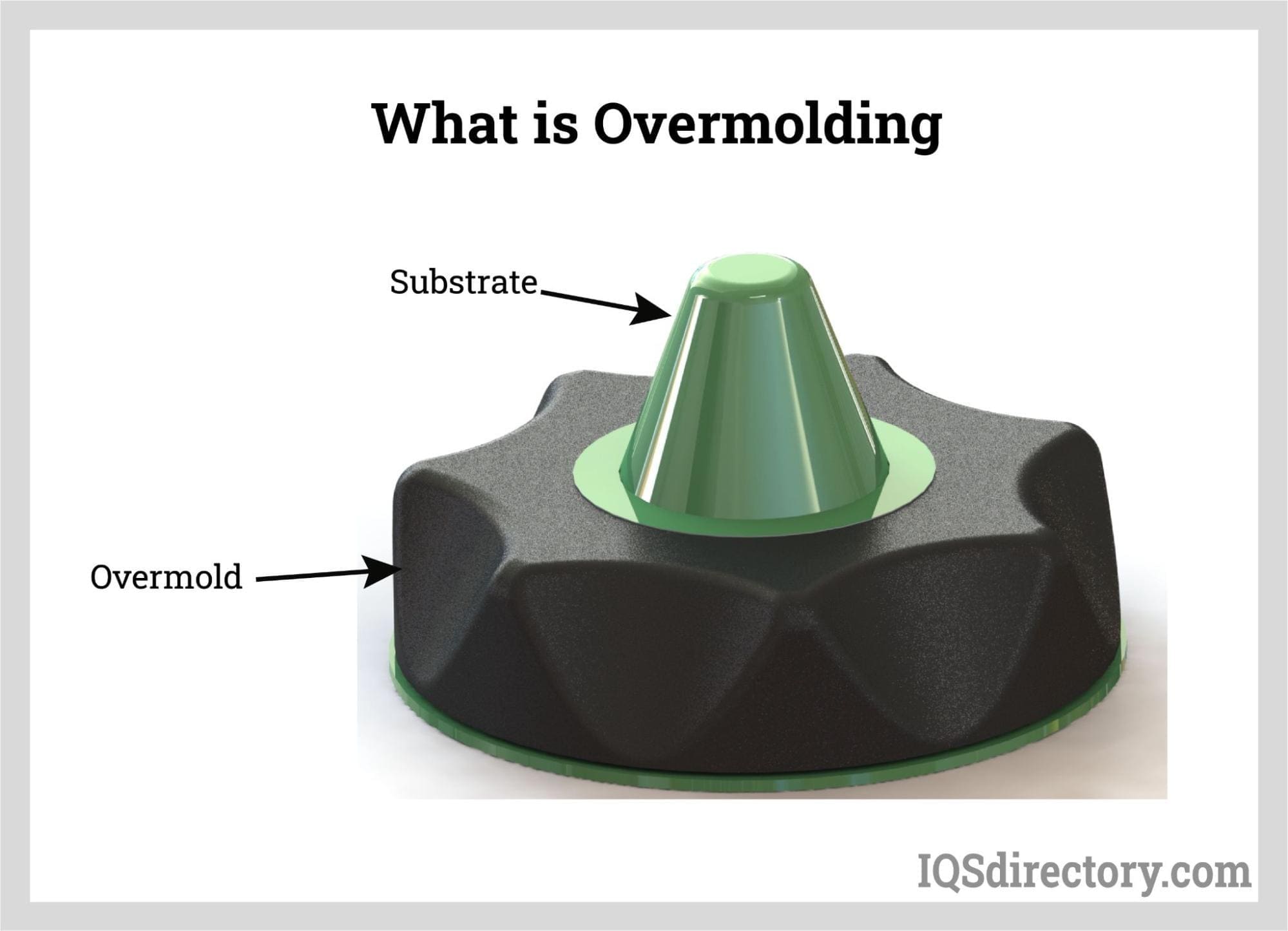
A leader in the plastic processing industry for over 70 years, Aptyx provides a range of manufacturing services including injection, blow and dip molding, extrusion, and assembly. Within injection molding we are deeply experienced in complex processes such as over molding, two-shot molding and insert molding. With a focus on delivering high-quality product and exceptional customer service, you...
Valencia Plastics is your leading full-service injection molded plastics manufacturer. Our products are made with various materials, including urethane, polyurethane, nylon, acrylic, and polycarbonate. We offer a wide range of sizes from miniature items up to 7 lbs. large parts. We are ISO 9001:2015 compliant. Industries we serve include electrical, military, automotive, aerospace, and...
Abtec, Inc. is a manufacturer of injection molded thermoplastics for high-tech OEMs. Since 1981, we have provided quality injection molded plastics and engineering services to such industries as automotive, aerospace, dental, electronics, food handling, nuclear, reprographics and more. Our 21,000 square feet building operates 24-hours a day, 5 days a week. Contact us today!

You won’t find better quality injection molded plastics anywhere else in the industry. We have built ourselves up from a small manufacturing company to a large company with decades of experience.
More Injection Molded Plastics Companies
Applications
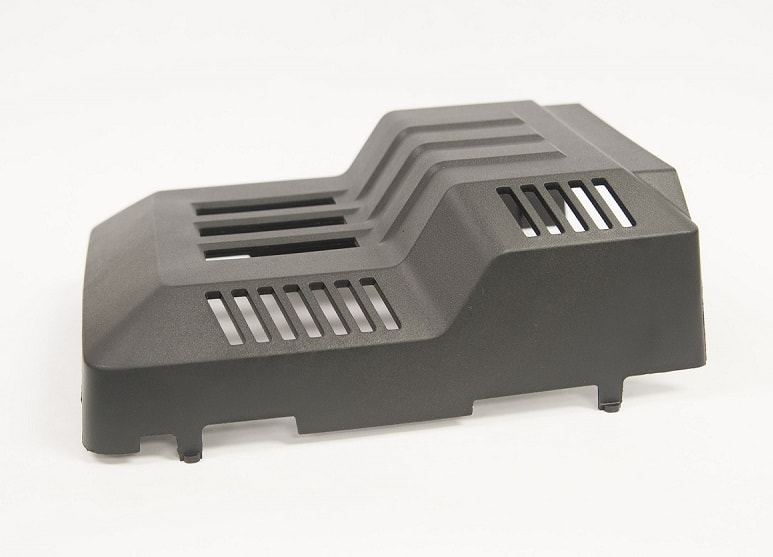
Injection molding is favored by customers who need intricately designed parts that are challenging to produce manually. Manufacturers also prefer it for its cost-efficiency in production and tooling. Consequently, injection molded plastics find myriad applications across diverse industries, including consumer products, household goods, electronics, automotive manufacturing, aerospace, sports and recreation, and healthcare.
Products Produced
Creating plastic products is not only possible but also encouraged, as long as a manufacturer can design a plastic mold cavity for it.
For example, a vast array of everyday household items are produced through plastic injection molding or custom injection molding processes. These include plastic containers, gaming cartridges, buckets, and tool handles. Beyond household items, many commercial, industrial, and medical products are also made using injection molding. Examples include vehicle bumpers, medical equipment, airplane parts, bottles, bike components, rubber balls, and various enclosures.
History
In 1872, John Wesley Hyatt and his brother Isaiah revolutionized manufacturing by inventing injection molding. Their initial machine was a straightforward design featuring a plunger that pushed plastic material through a heated barrel into a steel mold cavity, where it assumed its intended shape. Back then, mold creation was a laborious process, lacking in complexity. The primary plastic used was cellulose nitrate, a highly flammable material. Consequently, injection molding in the 1800s had its limitations, but it was still used to produce items like combs, collar stays, and buttons.
Fast forward to 1903, and we see another significant leap in the field. German chemists Theodore Becker and Arthur Eichengrun introduced soluble cellulose acetate, one of the first synthetic plastic materials. This invention provided manufacturers with a much safer and less flammable alternative, marking a significant advancement in the industry.
In 1919, Arthur Eichengrun, one of the pioneering chemists, patented his own version of the injection molding process, tailored for the first modern injection molding machines.
Although injection molded plastic products held great promise, the pre-World War II era saw limited diversity in plastic materials and a small customer base. The onset of WWII, however, sparked a surge in demand for plastic products essential to the war effort. This urgency drove chemists to rapidly develop new synthetic plastic formulas and prompted engineers to devise more efficient molding techniques. Answering this call, American inventor James Watson Hendry designed screw injection mold machines in 1946. Hendry’s innovation enabled manufacturers to produce parts with exceptional precision and minimal errors. It also allowed them to blend additives, such as pigments, into the raw plastic before molding. Today, screw injection molding machines remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
After World War II, the United States witnessed a remarkable economic surge, sparking an unprecedented demand for plastic products that had barely been on the radar before. This surge catapulted injection molding into a cornerstone of manufacturing. Today, this industry is still growing, with the number of custom plastic products increasing annually by about 750 since 1995. Alongside this, the variety of custom plastic materials has also expanded. A significant shift began in the late ’80s and early ’90s as the plastic industry embraced sustainable practices. This shift led to the abandonment of non-recyclable plastic materials and energy-intensive tooling procedures, marking a pivotal move towards eco-friendliness.
Materials
Typically, manufacturers perform the injection molding process using elastomers, thermoplastics, and thermosets. These broad categories encompass a diverse range of plastics. To delve deeper into these classifications and discover some of the most commonly utilized plastics in injection molding, explore the descriptions provided below.
Elastomers are materials with the unique ability to deform with ease compared to other solids and, upon cooling and hardening, maintain their elasticity and original strength. This remarkable trait is known as viscoelasticity. Versatile and adaptable, elastomers like nylon are highly favored for a wide range of applications.
Thermoplastics are versatile polymers that soften and become moldable with only moderate heat. Once cooled, these injection-molded parts solidify completely. However, they can be reheated and reshaped, allowing for corrections or modifications. These polymers boast a high molecular weight, making them particularly robust. Manufacturers favor thermoplastics due to their cost-effective tooling and production processes.
Thermosets are polymers that, once molded, resist any attempt at reshaping. Though they lack reusability, their extraordinary durability makes them ideal for high-temperature applications.
Polyethylene is a versatile thermoplastic known for its remarkable impact resistance, flexibility, and low friction. It excels as an electrical insulator, boasts low permeability, and resists many chemicals effectively. Among its common forms are high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). As the most extensively manufactured plastic globally, polyethylene finds widespread use in injection-molded packaging, bottles, and containers.
Polypropylene is a lightweight, chemically resistant thermoplastic that manufacturers favor for creating packaging. It’s also utilized in producing injection-molded items like car parts, medical devices, and lab equipment. Known for its impressive strength and high melting point, it’s ideal for containing hot liquids.
Nylon, a versatile thermoplastic elastomer, has been a staple in manufacturing since the 1930s. Known for its durability, it stands up to wear, chemicals, abrasions, friction, and extreme temperatures. This resilience makes nylon an ideal material for a wide range of injection-molded products, including automotive parts, medical devices like catheters, footwear, and sporting goods.
Epoxy resins, known for their thermoplastic nature, boast impressive weather, temperature, and corrosion resistance, alongside forming robust bonds. These versatile polymers are utilized by manufacturers to injection mold a variety of products including bottle caps, plastic cups, utensils, and kitchen tools. They are also key in crafting automotive parts, appliances, motor components, insulator parts, generator components, and furniture pieces.
Polystyreneis a cost-effective plastic known for its relatively low melting point. Available in both foamed and rigid varieties, this hard and brittle material is ideal for protective packaging, disposable cutlery, trays, bottles, tumblers, and lids. However, a significant disadvantage of polystyrene is its non-recyclability.
Phenolic resins, synthetic thermosetting polymers, were once the cornerstone of molded plastic products like laboratory countertops and billiard balls. However, their prominence has waned over time, overtaken by modern materials such as epoxy and fiberglass.
Process Details
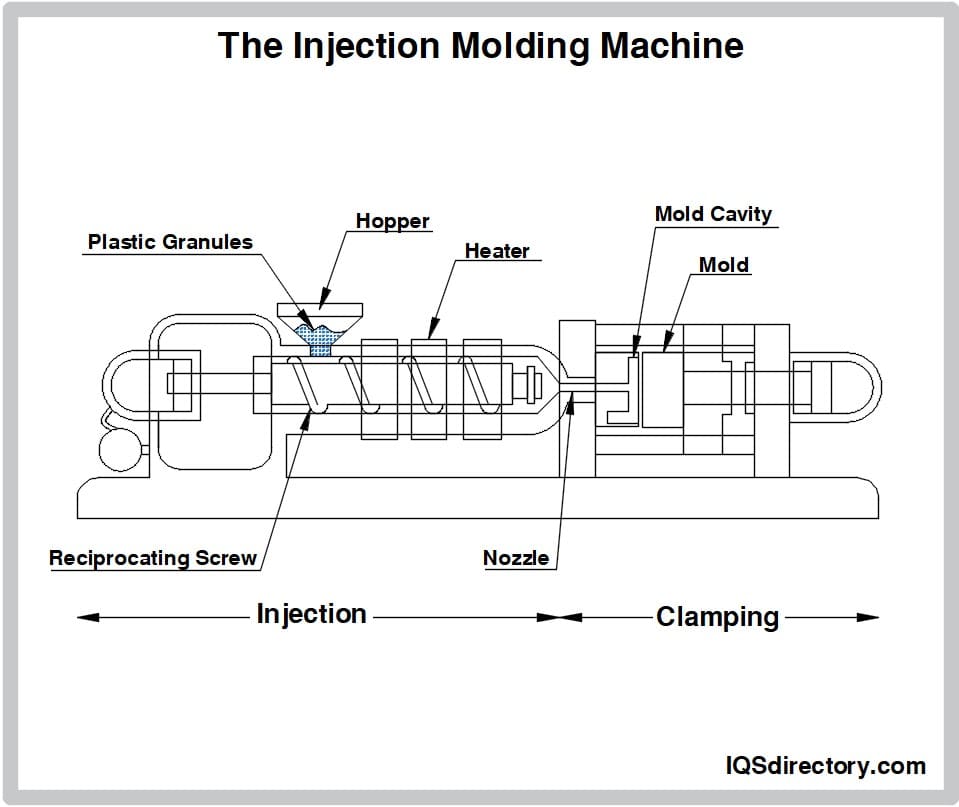
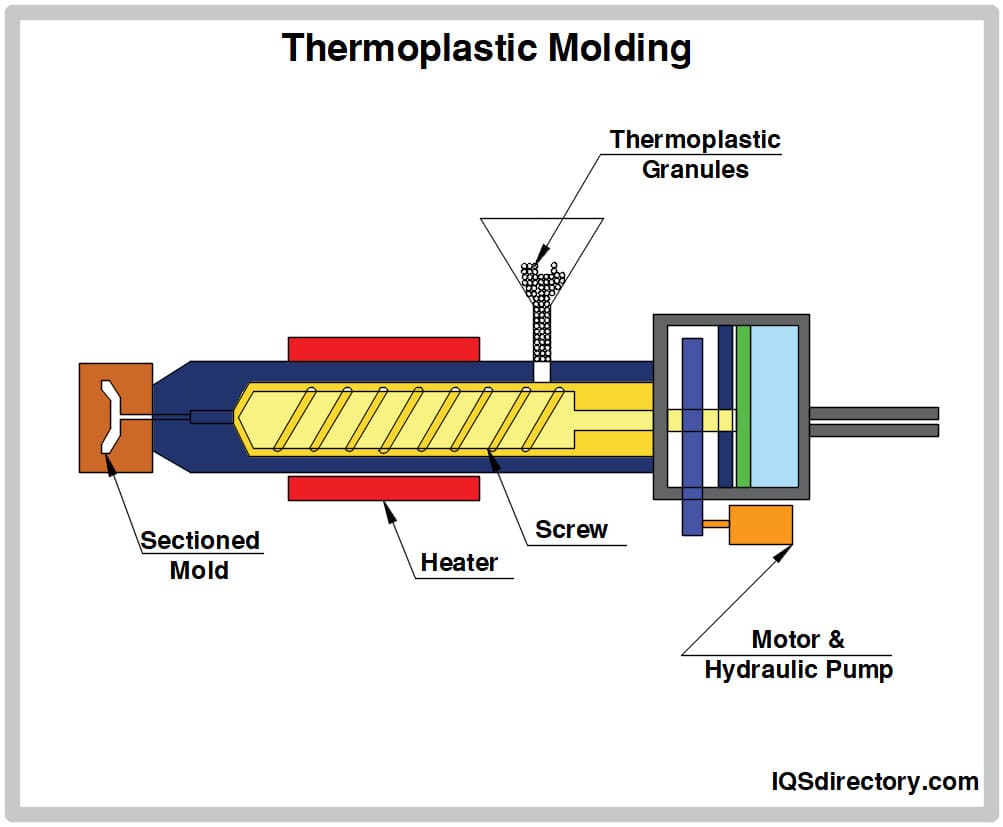
The plastic injection molding process unfolds through several essential stages: melting the plastic, injecting it into a mold, shaping it to the desired form, cooling it down, and finally, releasing the finished product.
1. Melting
At this stage, manufacturers transfer plastic from the hopper, where it waits its turn, to the heating unit. Here, the plastic is heated and stirred until it reaches a molten state. Once melted, additional chemical agents like dye can be incorporated to achieve the desired final appearance and texture of the product.
2. Injection
The subsequent phase of the production process is injection. In this stage, a screw, also referred to as an injector, employs mechanical or hydraulic pressure to drive the molten plastic into the mold cavity.
3. Shaping
Encased within the mold, the molten plastic flows seamlessly, conforming to the contours of the cavity. As it cools, it solidifies into its final form. Air bubbles, if trapped, can compromise the quality of the product. Fortunately, most molds are designed with features that allow these air bubbles to escape, ensuring a smooth finish.
4. Cooling
The use of cooling liquids around the molding chamber can speed up the cooling process and, consequently, the entire manufacturing procedure, as they effectively draw heat away from the plastic.
5. Releasing
Once the injection mold splits open, the freshly cooled and solidified plastic part is freed. Occasionally, a series of ejector pins or rods also need to be extracted from the mold. This entire removal process can vary, taking anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
6. Secondary Processing
Injection molded products typically emerge without the need for additional processing. However, there are exceptions. When the final product exhibits joining lines or other imperfections, a finishing procedure may be necessary. The extent of this finishing depends on the quality of the mold cavity and the material used during production.
Design
Before embarking on the injection molding process for a plastic product, manufacturers must navigate a series of crucial decisions. These decisions hinge on a variety of application and product specifications, including required material strength, anticipated chemical exposure, frequency of use, temperature tolerance, intended product lifespan, and the customer’s budget.
Based on these specifications, manufacturers determine the appropriate type of plastic material, the shape and dimensions of the product, the mold design, and whether to opt for custom injection molding. Custom injection molding involves creating a mold cavity tailored precisely to the consumer’s requirements, rather than using a pre-made design. Although this customization increases the cost of the generally economical injection molding process, the expense can be justified if the volume of your product order is substantial.
Variations and Similar Processes
Gas assist injection molding is a specialized form of plastic molding that uses an inert gas, like nitrogen, to create hollow sections within the mold, aiding the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavity.
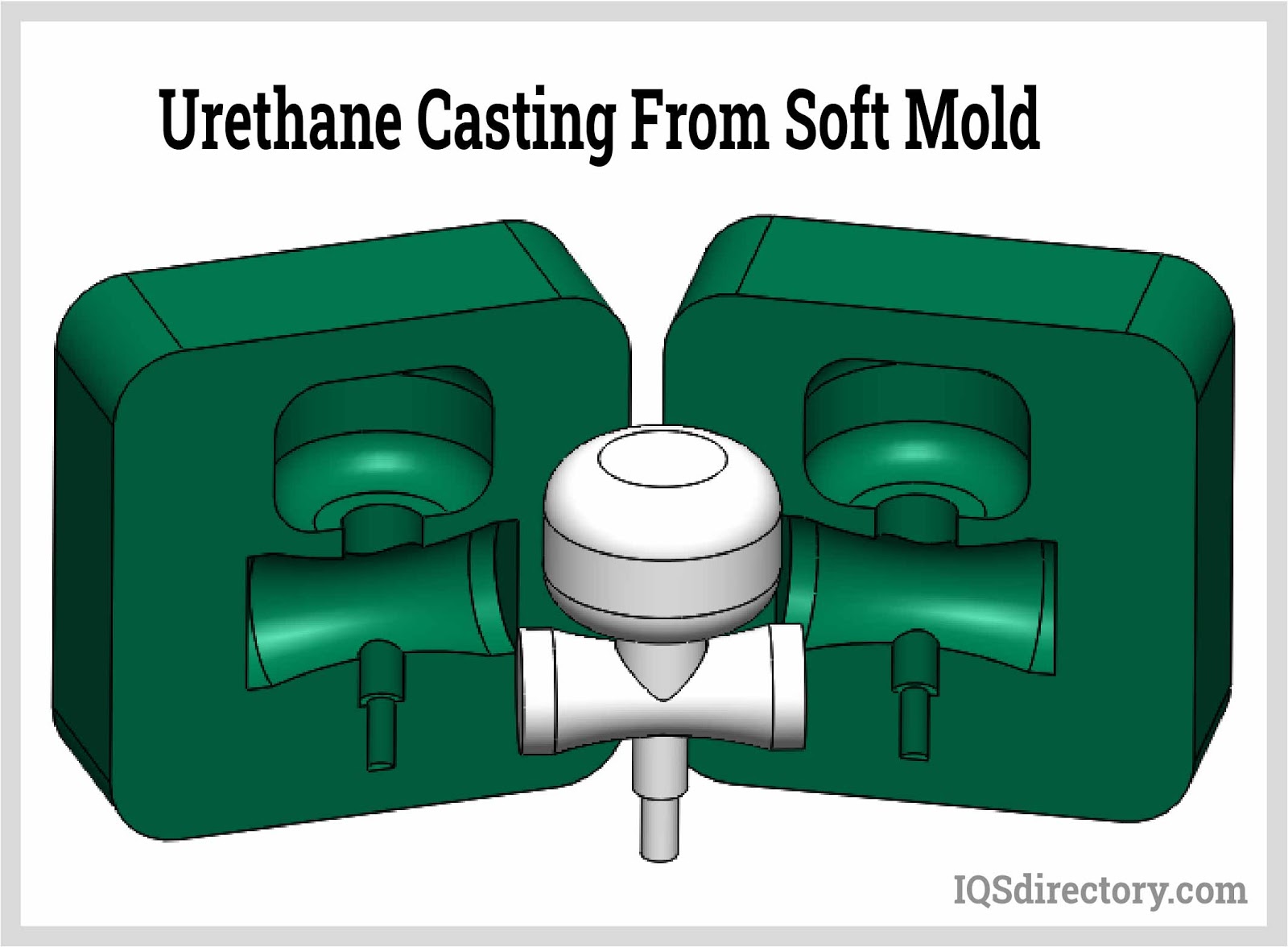
Reaction injection molding is a specialized variation of the standard injection molding process. It includes an extra step where the reaction injection molding machine introduces a curing agent into the mold cavity. This curing agent is crucial as it solidifies the material, ensuring that the finished product retains its shape and strength once it is removed from the mold.
Benefits
The plastic injection molding process brings a host of advantages to both manufacturers and end users. Firstly, injection molding stands out as highly cost-effective, especially when producing in bulk. The efficiency shines through when multiple parts are crafted from a single mold cavity, driving down costs significantly. Furthermore, a single mold cavity can be reused numerous times after its initial fabrication, consistently producing identical products with minimal variation. This not only conserves time, money, and resources but also makes injection molding the perfect choice for high-volume production runs.
One more benefit of injection molding is its consistency; the process undergoes minimal changes, and plastic parts typically require no additional finishing after being removed from the mold cavity. Additionally, it boasts low tooling costs. The method produces minimal waste, and any plastic scrap generated can be easily recycled. Due to the minimal need for human intervention, labor costs and associated risks are significantly reduced. Lastly, injection molding is highly versatile.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
If you’re considering getting an injection molded plastic part, partnering with a seasoned and trustworthy manufacturer is crucial. This ensures they grasp your requirements and deliver high-quality work at a fair price. To assist you in finding the perfect production team, we’ve curated a list of top-tier plastic part manufacturers. You can explore their profiles, contact details, and website links by scrolling up. Before diving in, we recommend you take a moment to draft your own list of needs—note down your specifications, standard requirements, budget, deadline, delivery preferences, volume requests, questions, and concerns. With this comprehensive list, you can easily evaluate whether a company meets your service and product needs. Once you’ve compiled your list, start browsing through our recommendations. Regularly refer to your specifications to shortlist three or four manufacturers whose services align best with your application. Reach out to each one and discuss your project thoroughly, leaving no detail overlooked. After these conversations, compare your findings and choose the manufacturer that best fits your needs.
Check out our Injection Molded Plastics website
Check out our Polyurethane Molding website




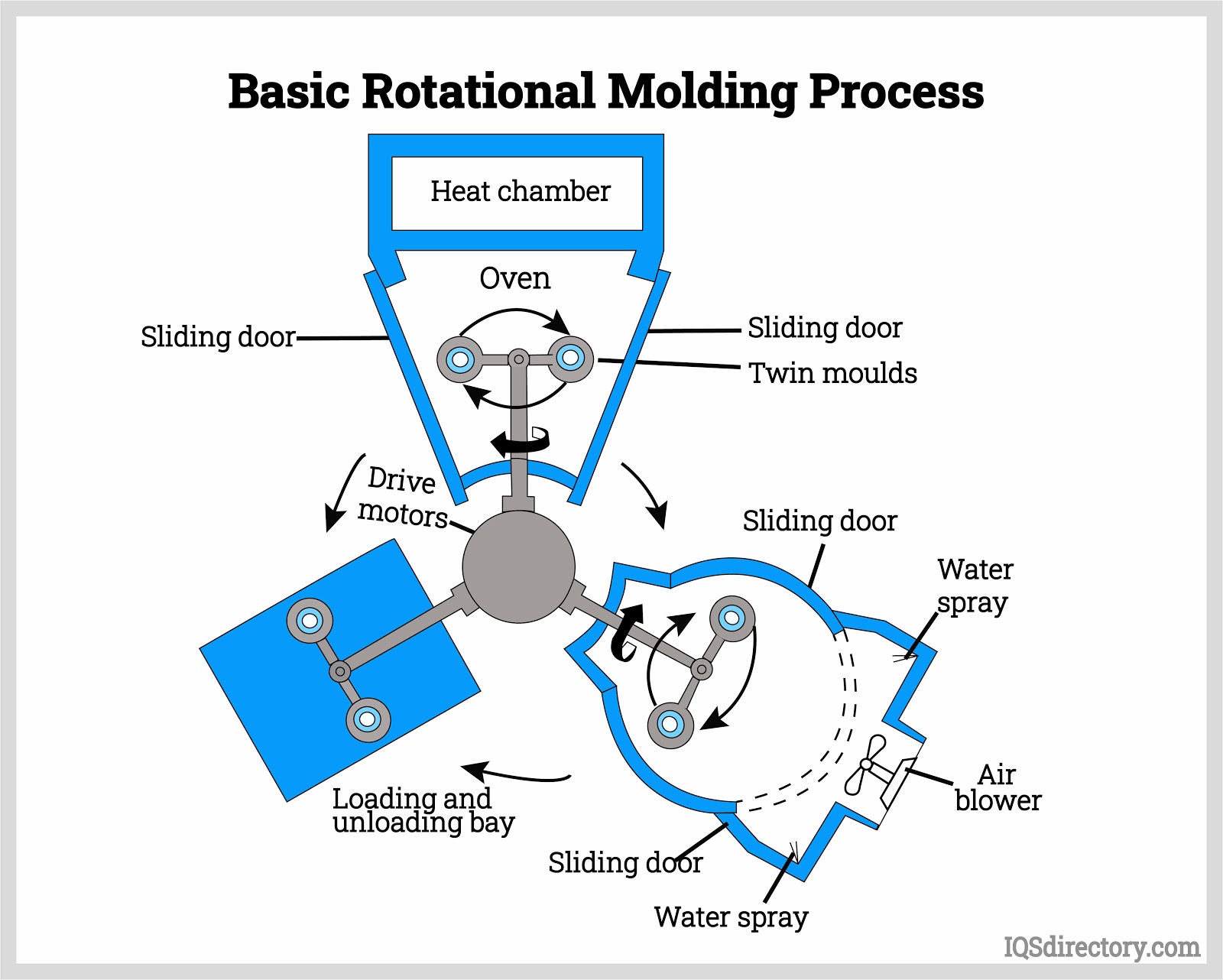
 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators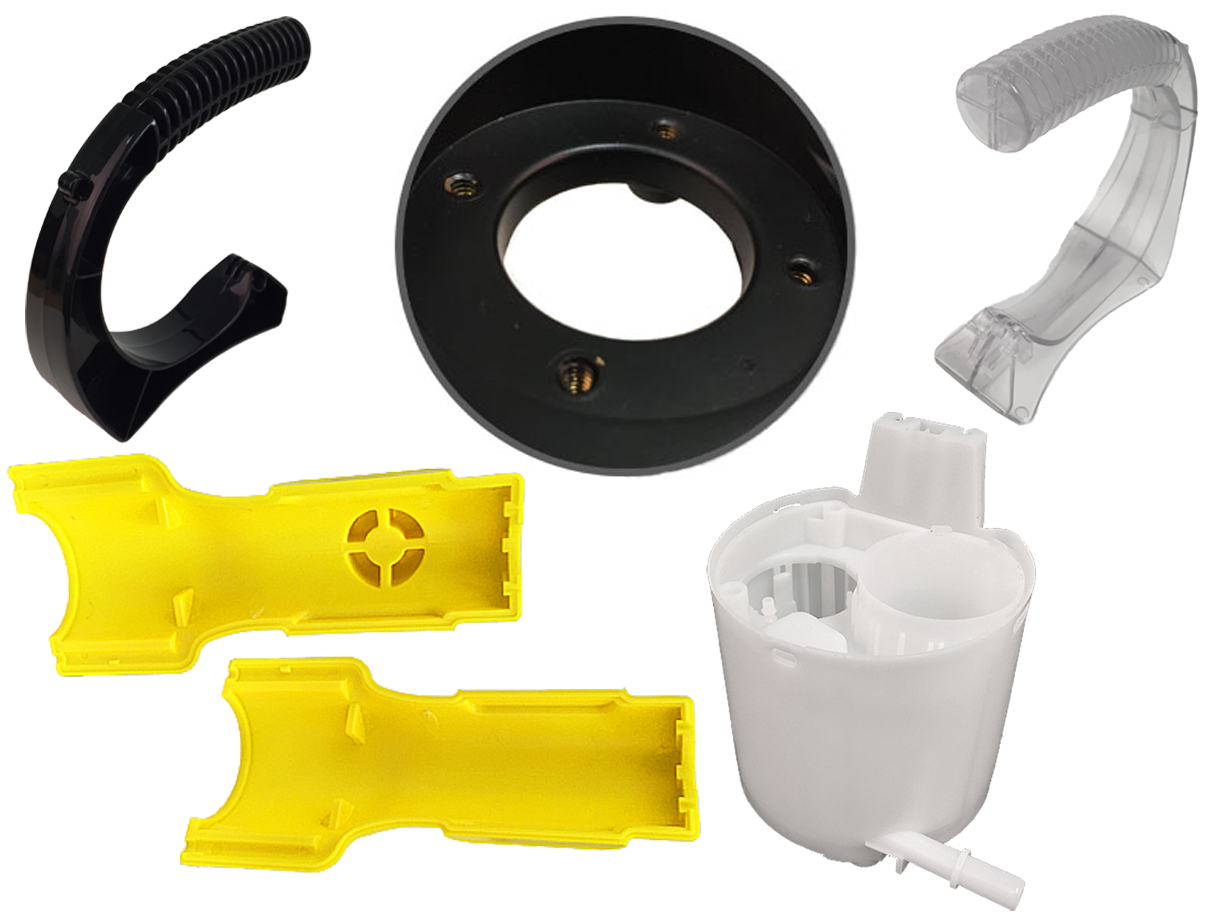 Injection Molded Plastics
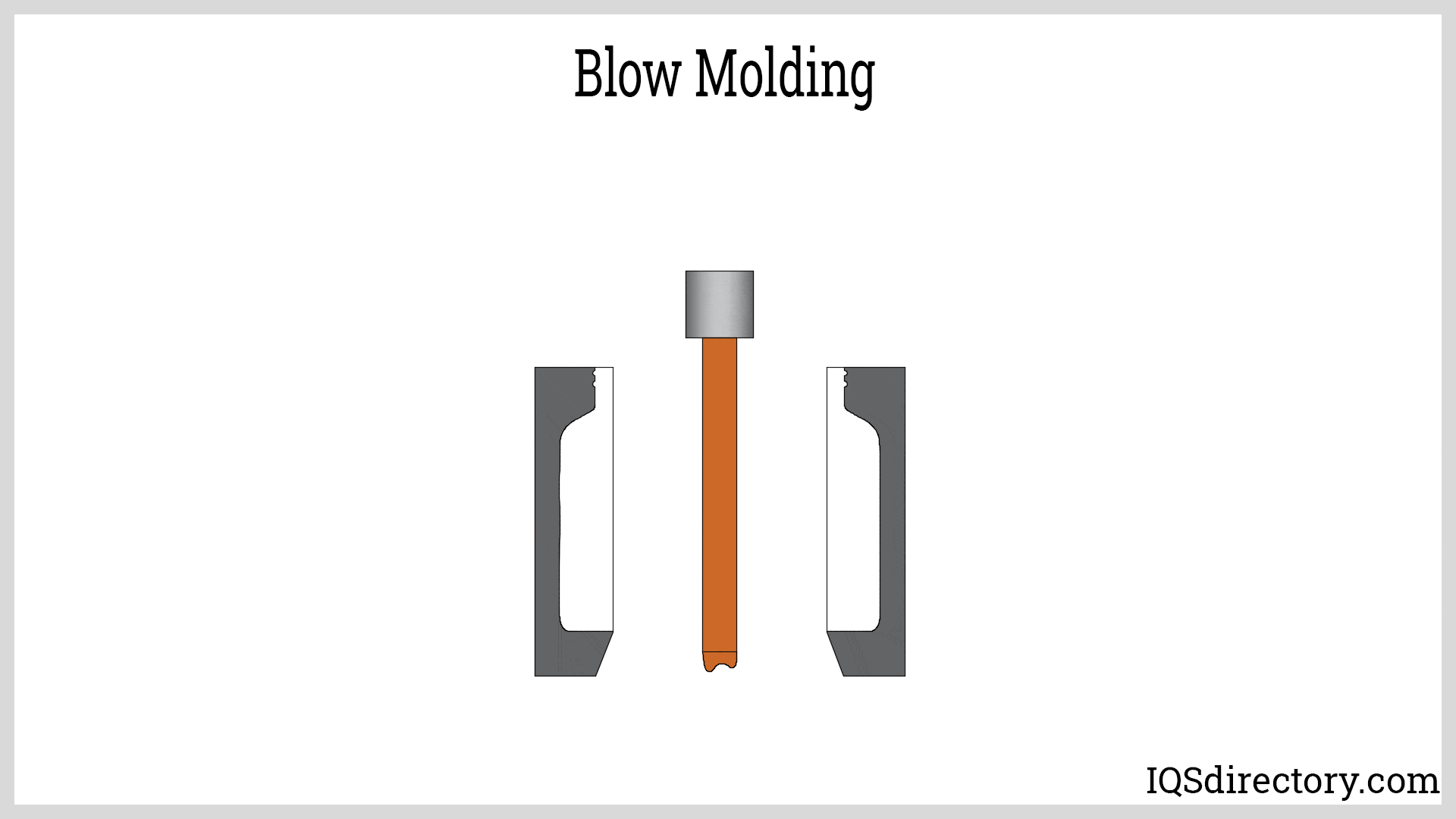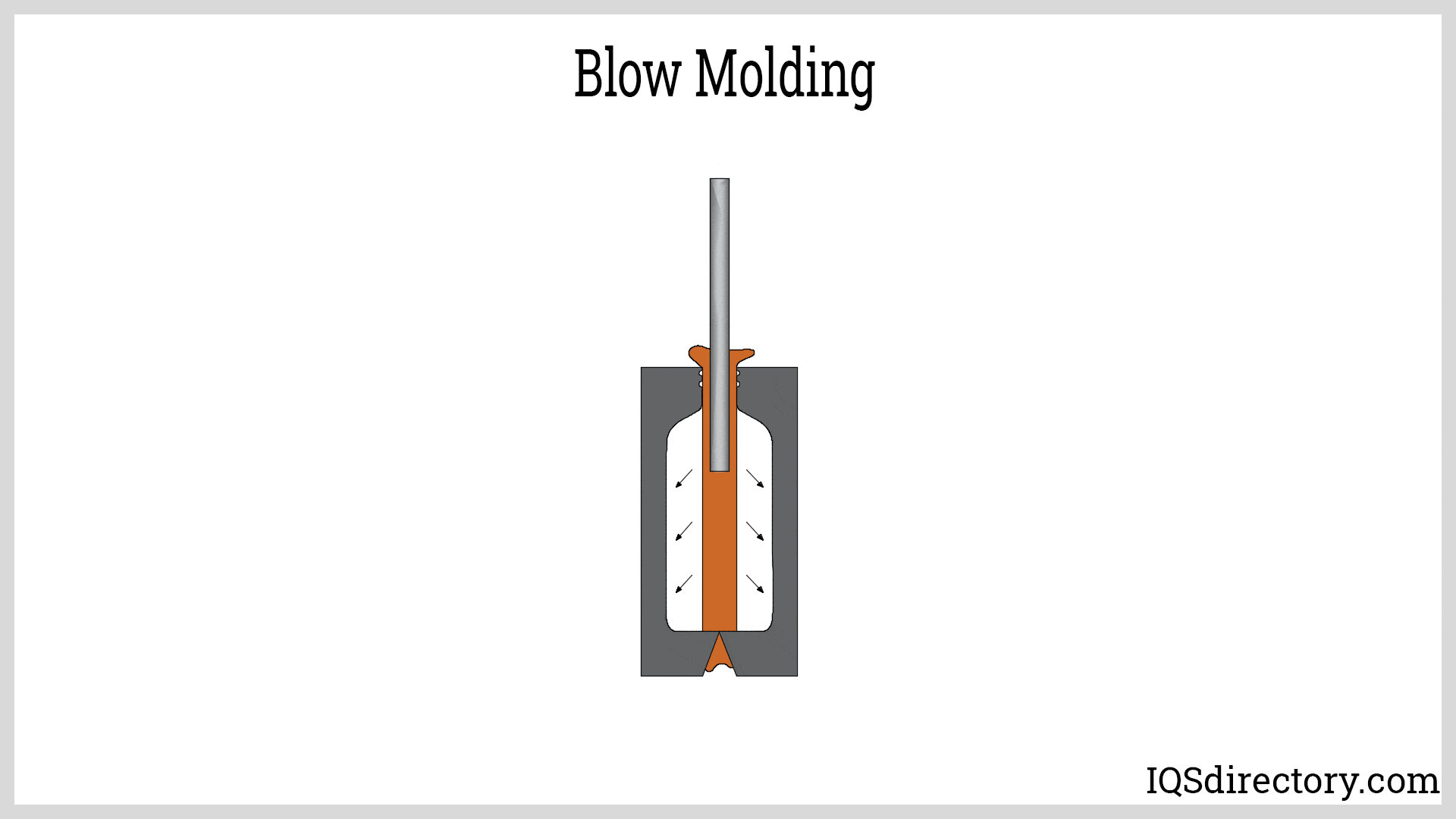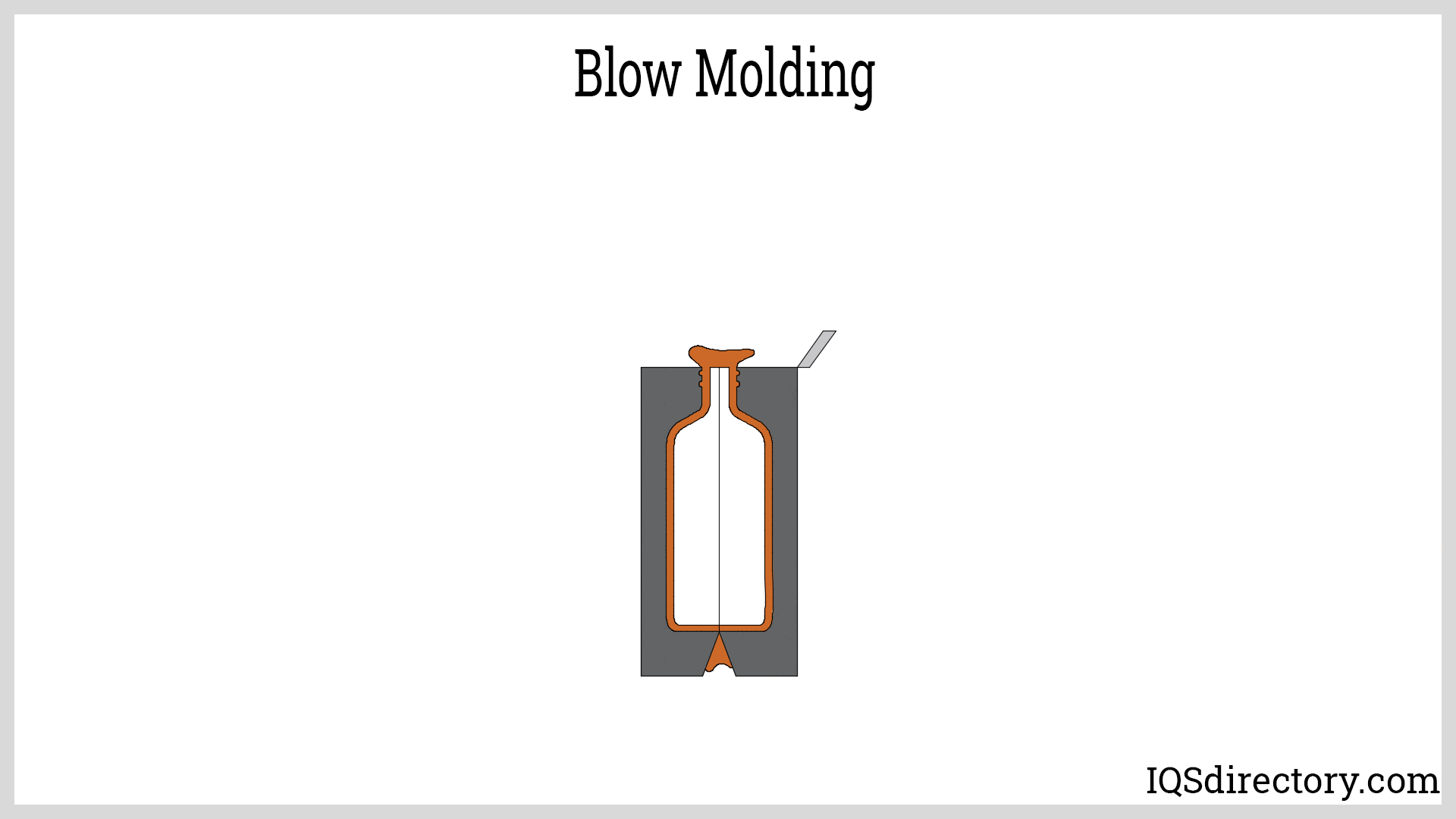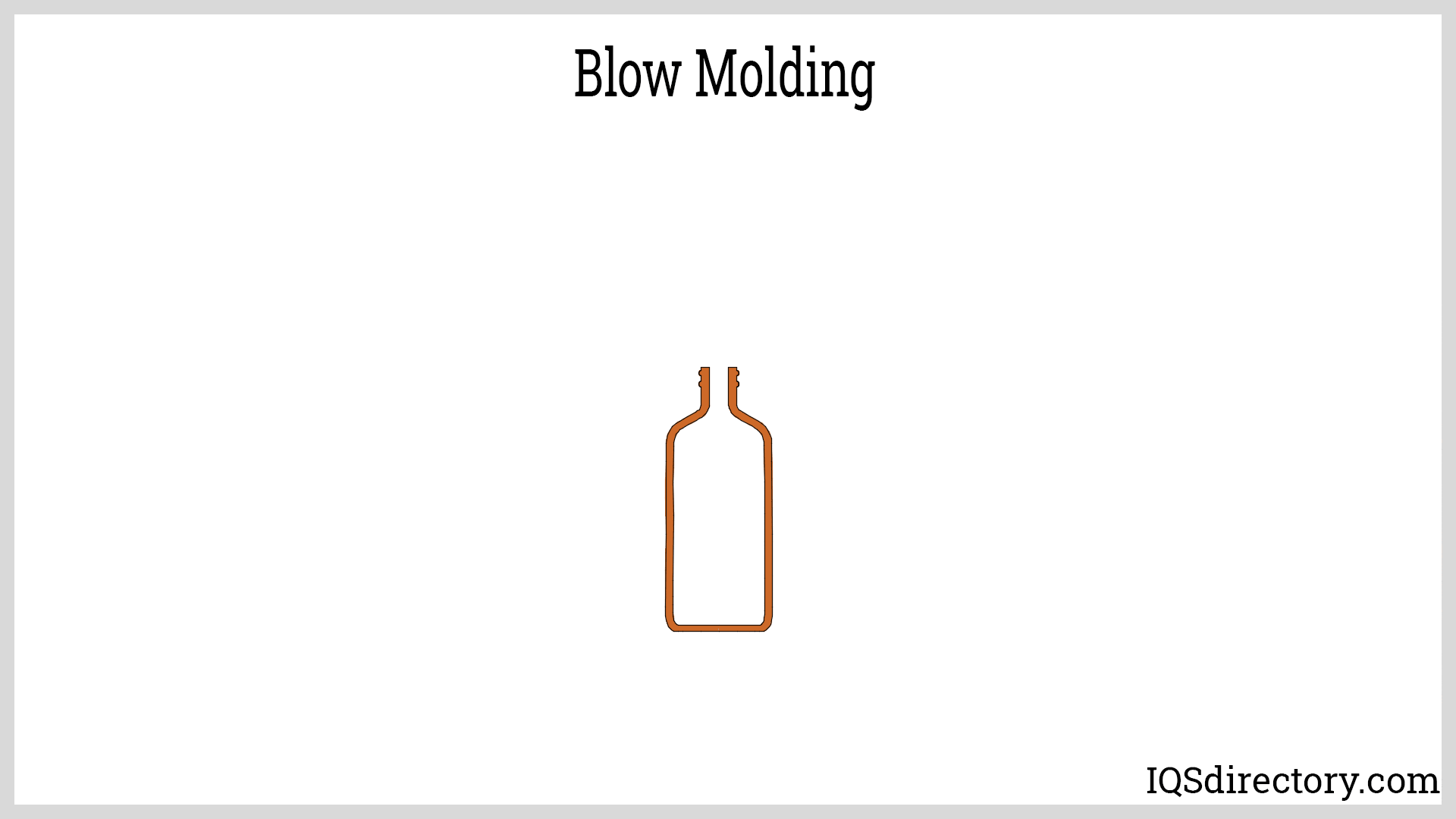
Injection Molded Plastics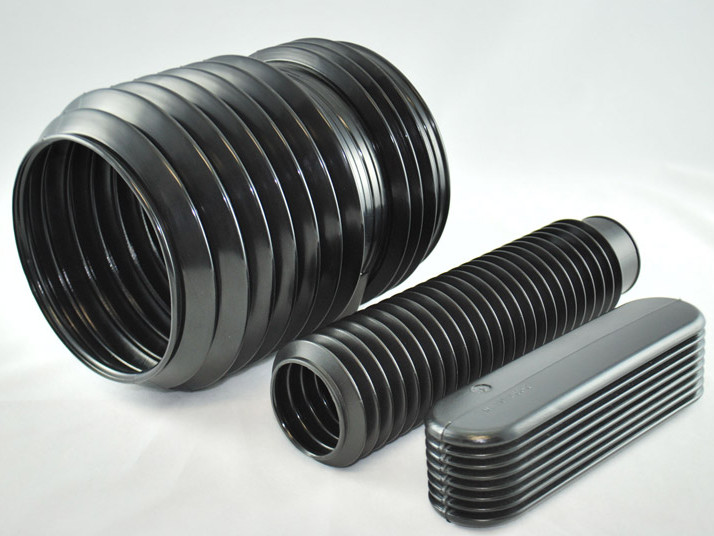 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding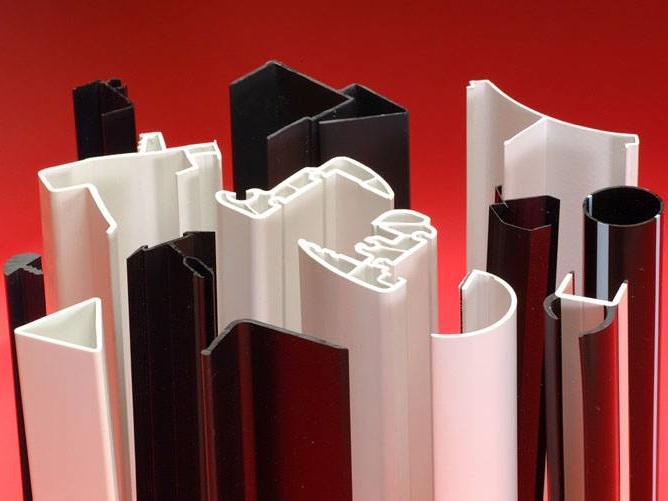 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding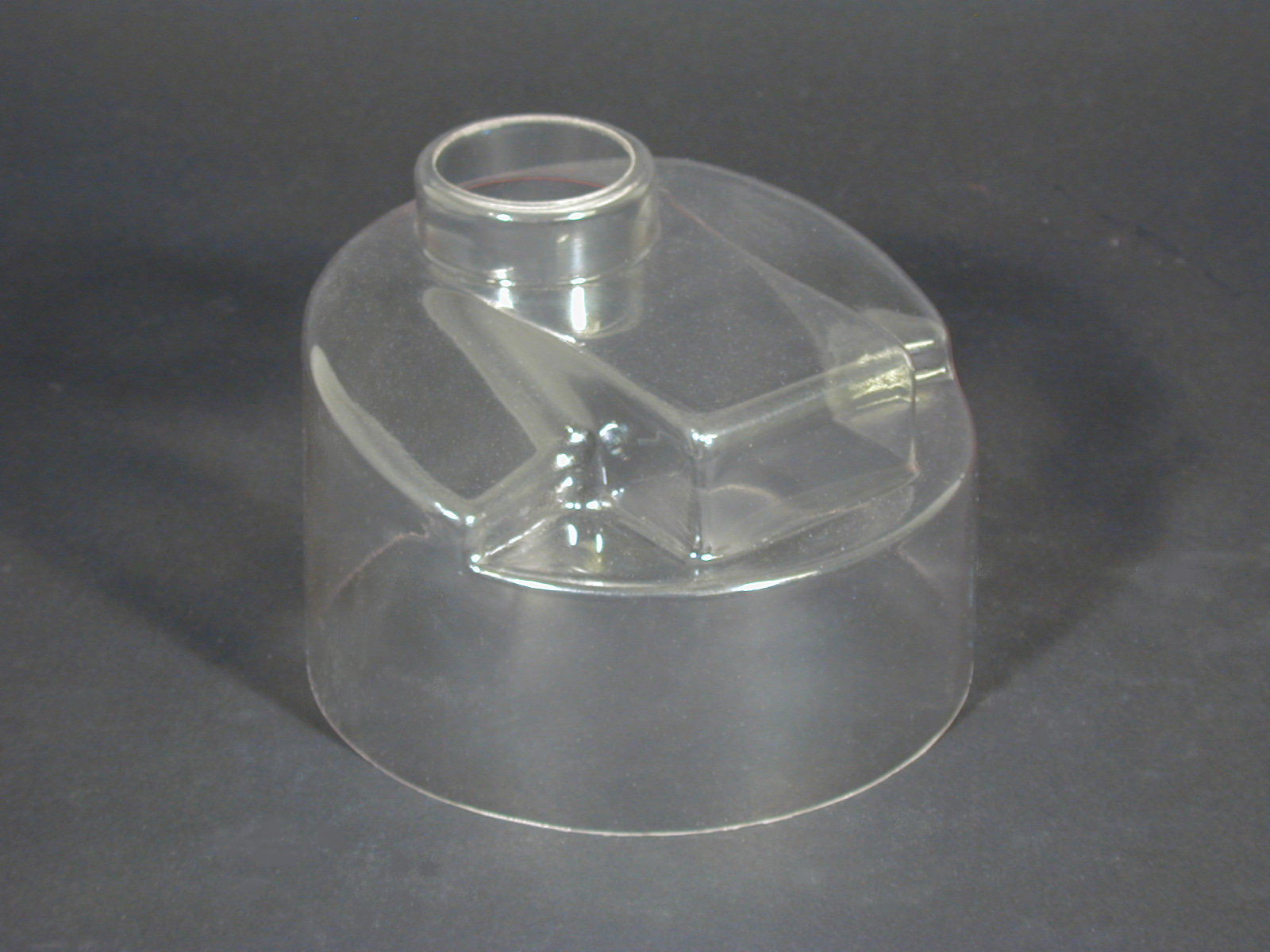 Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services